
DRI
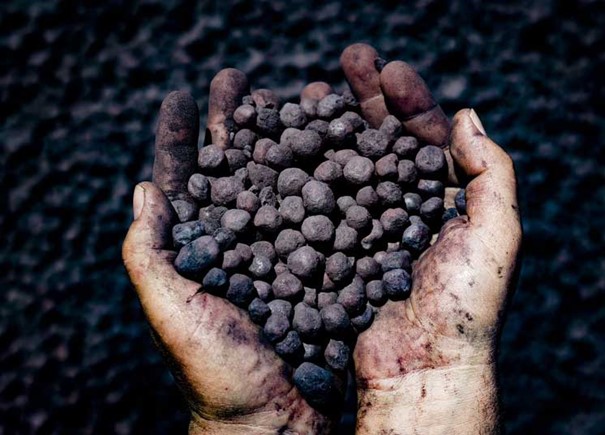
The name “sponge iron” or DRI may seem strange to some, while others may have heard this name in the news or seen it on commodity exchange boards. Over the past few years, the trading of this product has flourished and become a very attractive option for buyers in the iron and steel industry. What is Sponge Iron? This type of iron, also known as porous iron, is obtained through direct reduction of iron ore. In this production method, oxygen is removed from iron ores, and the final product will be in the form of spherical and porous lumps.
The presence of these voids and porosity in this iron gives it a sponge-like appearance, which is why it is called sponge iron. The high grade of porous iron makes it a suitable substitute for scrap iron and attracts a lot of attention from specialists. In the following article, the characteristics, production method, applications, protection methods, and other related information about this product will be discussed, providing comprehensive information for interested individuals.
What is DRI?
Porous iron or sponge iron, with its porous structure and high iron content, is the result of the direct reduction process of iron ore in direct reduction furnaces (DRF). These types of iron ores are often added to the furnace in the form of pellets, briquettes, or other smaller particles to be converted into sponge irons using reducing gases, such as natural gas.
In fact, the iron ores extracted from the earth are iron oxide rocks from which their oxygen is removed through the natural reduction process. In this process, iron oxide rocks are heated with carbon, creating a porous surface that resembles a sponge, hence the name “sponge iron.” Currently, about 5% of global steel production is produced using sponge iron, and this daily production is increasing.

History of Sponge Iron
The use of sponge iron in induction furnaces in Iran dates back to 1389 (2010). At that time, due to the availability of scrap iron, there was no shortage of iron in the country. However, India and China, during that period, due to the decline in the efficiency of their furnaces, stopped using induction furnaces, which they had sold to Iran, and did not find the use of these furnaces cost-effective. This led one of the factories in Yazd in 1389 to switch to the use of sponge iron.
Initially, many other factories also used this type of raw material but faced negative feedback. However, after some time, many factories started incorporating this product as their main raw material. The reason for the factories’ initial opposition was their lack of familiarity with sponge iron and its production method. Another reason was the presence of phosphorus and sulfur in sponge iron compared to scrap iron, which disrupted the melting analysis and increased the melting time.
Advantages of Using Sponge Iron
As mentioned, around 5% of the raw material available in the global iron market is sponge iron. This statistic demonstrates the high importance of this product in various industries. So, what are the advantages of this product? The following are some of the key advantages of sponge iron:
- This type of iron is one of the best alternatives to scrap iron.
- The cost of using direct reduction units and induction furnaces is much lower compared to blast furnaces.
- The use of a blast furnace has higher biodegradability compared to the direct reduction method.
- The grade and purity of sponge iron will be much higher compared to other iron products.
- The transportation of sponge iron in the form of hot briquetted iron (HBI) is very convenient and hassle-free.
- Natural gas can be used without separating impurities to produce this type of iron using the direct reduction method.
- Sponge irons have significant economic advantages, and their use in small-scale.
Applications of Porous Sponge Iron
Given the recent shortage of iron scrap for the production of billets and other steel products, finding a suitable substitute is of great importance. Sponge iron is one of the best materials used to replace scrap iron in induction furnaces for the production of these products. Currently, 50% of the capacity of induction furnaces is filled with sponge iron, while the remaining portion is supplied by iron scrap. Furthermore, compact forms of sponge iron, called briquettes, have facilitated transportation and storage. Additionally, these compressed sponge iron materials exhibit greater resistance to wear and corrosion, with reduced likelihood of porosity and surface detachment. Depending on the materials and temperature used in their production, three types of briquettes exist: hot briquettes, cold briquettes, and soft briquettes. Hot briquettes, produced at temperatures higher than 650 degrees Celsius, are the most widely used type.
Cold and soft briquettes, on the other hand, are produced at ambient temperatures and have different applications. In general, briquettes are used in various industries such as iron and steel, minerals, chemicals, fertilizer production, and hygiene products.

FAQs
In its pasty state, this type of iron is highly flammable and prone to oxidation and corrosion.
These products are produced in sizes ranging from 4 to 20 millimeters and have a density of 4.3 to 6.3 metric tons per cubic meter. Their bulk density ranges from 6.1 to 9.1 metric tons per cubic meter.
Natural gas or coal is used in the production process. When natural gas is used, methods such as Midrex, HYL, and Proxir are employed. When coal is used, SL/RN, DRC, and Jindal methods are utilized.
Currently, India is the largest producer of various types of sponge iron worldwide.
Final Remarks
Sponge iron is one of the primary raw materials used in various industries and is obtained through the concentration or pelletization processes of iron ore. Due to its high production volume and relatively low price in Iran, it has become one of the most suitable products for export, yielding significant profits. However, the price of this product is influenced by global and domestic economic conditions. For further information, users can fill out the contact form on the kaladasht.com website to have their questions answered by the company’s experts.